Chained for Attack: OpenVPN Vulnerabilities Leading to RCE and LPE

Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, virtual private networks (VPNs) are often considered a cornerstone of secure communications. OpenVPN, a widely adopted open-source VPN solution, is integrated into millions of devices worldwide, including routers, PCs, and smart devices. However, recent discoveries have unveiled vulnerabilities that could expose OpenVPN users to significant risks. Microsoft researchers have identified multiple vulnerabilities in OpenVPN that, when chained together, could lead to remote code execution (RCE) and local privilege escalation (LPE). These vulnerabilities, assigned CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures), emphasize the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures.
What is OpenVPN?
OpenVPN is a highly versatile VPN system that creates private, secure connections between networks using the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption protocol. It supports AES-256 encryption, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity. OpenVPN’s open-source nature allows extensive audits and integration across various platforms, including Windows, Android, macOS, iOS, and BSD. Its flexibility has made it a popular choice across industries such as IT, finance, telecommunications, and beyond.
Despite its robust security reputation, vulnerabilities in OpenVPN’s components demonstrate that even the most trusted solutions require continuous monitoring and improvement. Let’s delve into the specific vulnerabilities uncovered.
Discovered Vulnerabilities
The research highlighted four key vulnerabilities in OpenVPN, each with unique implications. These vulnerabilities were publicly disclosed in 2024, with associated CVEs assigned as follows:
1. CVE-2024-27459
Description: A stack overflow vulnerability in Windows.
Impact: Can lead to denial-of-service (DoS) attacks and local privilege escalation (LPE).
Component Affected: Windows Terminal Access Point (TAP) driver.
Release Date: January 2024.
2. CVE-2024-24974
Description: Unauthorized access to the \\openvpn\\service named pipe in Windows.
Impact: Allows attackers to remotely interact with the named pipe and perform unauthorized operations.
Component Affected: openvpnserv service.
Release Date: January 2024.
3. CVE-2024-27903
Description: A flaw in the plugin mechanism.
Impact: Enables remote code execution (RCE) on Windows and LPE/data manipulation on Android, iOS, macOS, and BSD.
Component Affected: openvpnserv service and plugin mechanism.
Release Date: January 2024.
4. CVE-2024-1305
Description: A memory overflow vulnerability.
Impact: Results in denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
Component Affected: Windows TAP driver.
Release Date: January 2024.
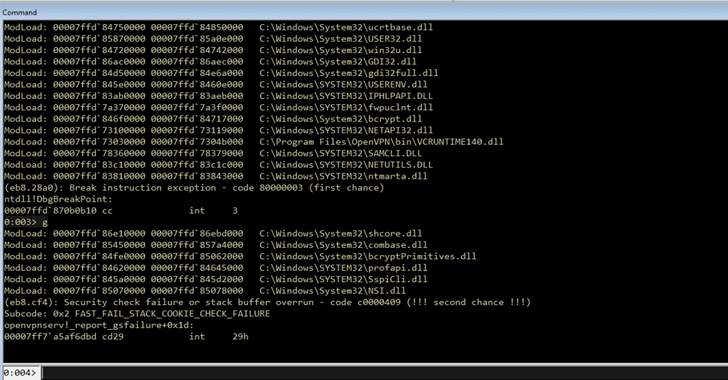
Exploitation and Attack Chains
To exploit these vulnerabilities, attackers typically require access to a user’s OpenVPN credentials. Such credentials can be acquired through methods like:
- Purchasing stolen credentials on the dark web.
- Deploying stealer malware to harvest credentials.
- Sniffing network traffic to capture NTLMv2 hashes and cracking them using tools like HashCat or John the Ripper.
Once credentials are obtained, attackers can chain the vulnerabilities to achieve sophisticated attack scenarios.
Remote Code Execution (RCE)
To execute RCE:
- The attacker uses stolen credentials to issue a NET USE command, accessing the target’s operating system resources.
- They gain control over the \\openvpn\\service named pipe and send a “connect” request to launch a new instance of openvpn.exe.
- Malicious commands are executed, leading to remote code execution.
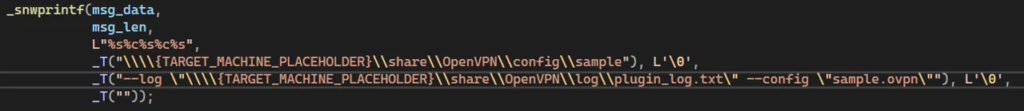
Local Privilege Escalation (LPE)
To achieve LPE:
- The attacker creates a malicious configuration file and loads it into the OpenVPN launching process.
- By connecting to the \\openvpn\\service named pipe, the attacker instructs openvpnserv.exe to run openvpn.exe with the malicious configuration.
- This grants elevated privileges, allowing deeper system compromise.

Security Implications
The vulnerabilities highlight critical weaknesses in the openvpnserv service and the Windows TAP driver. Attackers could combine CVE-2024-24974 with CVE-2024-27903 or CVE-2024-27459 with CVE-2024-27903 to form potent attack chains. These flaws underscore the importance of securing VPN solutions and the systems they integrate with.
Mitigation and Protection Guidance
Addressing these vulnerabilities requires a multi-faceted approach:
1. Apply Patches
- Action: Update OpenVPN installations to the latest patched versions—2.5.10 and 2.6.10.
- Resource: Visit the OpenVPN website for official patches.
2. Segment and Restrict Access
- Disconnect OpenVPN clients from the internet when not in use.
- Limit access to authorized users only.
3. Strengthen Credentials
- Enforce strong password policies for OpenVPN accounts.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible.
4. Monitor and Harden Systems
- Ensure proper segmentation of devices running OpenVPN.
- Reduce the number of users with write permissions to authentication configurations.
- Monitor for suspicious activity and credential theft attempts.
Broader Implications for Open-Source Security
The discovery of these vulnerabilities in OpenVPN highlights both the strengths and challenges of open-source projects. On one hand, the transparency of open-source code allows vulnerabilities to be identified and resolved quickly. On the other hand, the widespread adoption of such projects increases the potential impact of discovered flaws.
Organizations relying on open-source solutions must implement robust vulnerability management practices. Regular updates, proactive threat assessments, and strong access controls are vital to mitigating risks associated with open-source software.
Closing Summary
The vulnerabilities discovered in OpenVPN serve as a stark reminder that no software is immune to exploitation. By chaining flaws like CVE-2024-24974, CVE-2024-27903, CVE-2024-27459, and CVE-2024-1305, attackers can achieve devastating outcomes, including RCE and LPE. Organizations using OpenVPN should prioritize patching and adopt robust cybersecurity practices to safeguard their systems.
In the era of advanced cyber threats, vigilance and proactive measures are essential to maintain the integrity and security of critical infrastructure. OpenVPN’s response to these vulnerabilities underscores the importance of continuous improvement in the face of evolving challenges, ensuring that it remains a trusted solution for secure communications.
Related posts:
- Windows Snip & Sketch/Snipping Tool Vulnerability (CVE-2023-28303)
- Addressing Critical Vulnerabilities in VMware vCenter Server
- How to Uninstall Teams Classic from all user profile
- Windows Secure Kernel Mode Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
- Understanding Vulnerabilities, Exploits, and Threats
- Birthday attacks against TLS ciphers with 64bit (Sweet32)
- January 2025 Patch Tuesday forecast: Changes coming you need to know
- [Solved] CVE-2024-12686 BeyondTrust Privileged Remote Access (PRA) and Remote Support (RS) OS Command Injection Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-23040: GitHub Desktop Credential Leak Vulnerability (GHSA-36mm-rh9q-cpqq)
- A Comprehensive Guide to WinGet: The Windows Package Manager
